A closer look at 5-HTP and its brain-boosting benefits
10/07/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

The supplement 5-HTP is touted by many for its brain benefits, which include enhanced cognitive function and the treatment of depression, anxiety, and insomnia, among others. While many people believe in and advocate the use of this supplement, many also insist that there is a lack of scientific evidence to back its purported benefits. So what are the brain-boosting benefits of 5-HTP and what were they based on?
The basis of 5-HTP’s health benefits
5-HTP stands for 5-hydroxytryptophan, an amino acid naturally synthesized by the body. Unlike some beneficial molecules, 5-HTP is not obtained from food. However, tryptophan, the amino acid needed by the body to produce 5-HTP, only comes from certain food sources.
Tryptophan can be obtained from animal-based foods that are rich in protein, such as poultry, seafood, meat, eggs, and dairy products. Meanwhile, the supplement 5-HTP is produced from the African shrub Griffonia simplicifolia, the most abundant external source of the compound.
According to numerous accounts, 5-HTP is a great supplement that helps treat a variety of conditions. In the U.S., 5-HTP is used for anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, migraines, insomnia, ADHD, and fibromyalgia. 5-HTP is also said to aid in weight loss by reducing the appetite.
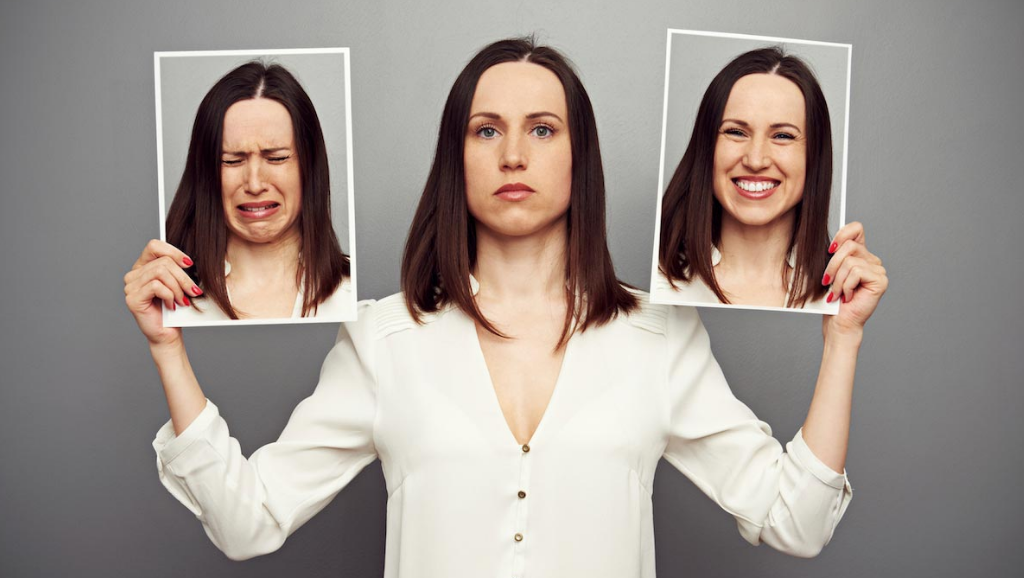
The potential of 5-HTP to help with various conditions stems from its ability to be converted into two useful compounds: serotonin and melatonin. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter associated with happiness and a positive mood while melatonin is a hormone related to sleep.
Reports about 5-HTP’s positive effects on anxiety and depression are linked to serotonin. Several studies have shown that people with low amounts of serotonin are more prone to suffer from depression and anxiety disorders. They are also likely to have insomnia, low self-esteem, negative thoughts, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and even seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Because 5-HTP can increase serotonin levels, many people believe that supplementing with 5-HTP can reduce the symptoms of anxiety and depression. (Related: Can 5-HTP really curb depression and anxiety?)
Melatonin is also linked to the treatment of depression, as well as improved brain function. Research suggests that this hormone, besides regulating sleep, also acts as a natural antidepressant. Impressive properties such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immune-enhancing, and neuroprotective effects have also been associated with melatonin.
Melatonin is synthesized by the body using serotonin. Melatonin controls the circadian rhythm and is responsible for telling the body to prepare for sleep. Because of its role and relationship with serotonin, the ability of 5-HTP to treat insomnia and other sleep disorders is most likely linked to melatonin.
However, only a few studies have looked into the potential of 5-HTP in treating mental disorders. Hence, skeptics who vocally question the health benefits of 5-HTP abound.
Other potential uses for 5-HTP
Despite having only a small number of studies supporting its claims, many people still swear by 5-HTP. Besides promoting sleep and improving the mood, 5-HTP could potentially be used for the following:
- Improving symptoms of fibromyalgia
- Reducing the frequency of migraines
- Relieving pain due to chronic headaches
- Alleviating premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Managing menopausal symptoms
- Reducing alcohol and drug withdrawal symptoms
- Managing nervous system disorders
- Improving symptoms of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease
Sources include:
Tagged Under: 5-HTP, 5-hydroxytryptophan, alcohol withdrawal, alternative medicine, anti-obesity, Anxiety, anxiety relief, beatdepression, brain function, brain health, brain health boost, brain nutrients, chronic headaches, cognitive health, dementia, depression, drug withdrawal, fibromyalgia, fightobesity, insomnia, melatonin, menopausal symptoms, Mental Disorders, mental health, migraines, natural cures, natural medicine, nervous system, Parkinson's Disease, premenstrual syndrome, remedies, serotonin, side effects, sleep disorders, stress relief, supplements, tryptophan
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 DEPRESSIONSYMPTOMS.NEWS
All content posted on this site is protected under Free Speech. DepressionSymptoms.news is not responsible for content written by contributing authors. The information on this site is provided for educational and entertainment purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional advice of any kind. DepressionSymptoms.news assumes no responsibility for the use or misuse of this material. All trademarks, registered trademarks and service marks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.